Technical SEO mistakes can silently damage your website’s performance and visibility. In 2025, these errors are especially costly as search engines become increasingly sophisticated in evaluating site quality and user experience. Our comprehensive guide identifies the most damaging technical SEO mistakes affecting websites today, with recent studies showing 95.2% of websites facing redirect issues and 80.4% lacking proper alt attributes. Let’s explore the critical technical errors you need to fix immediately to improve your rankings and user experience.
What Are the Most Damaging Technical SEO Mistakes?
The most devastating technical SEO mistakes prevent search engines from properly crawling, indexing, and ranking your website. According to recent studies, the most harmful issues include crawling/indexing restrictions, mobile responsiveness failures, poor page experience signals, and structural issues like redirect chains and duplicate content. These foundational problems can undermine all other SEO efforts, no matter how strong your content or backlink profile might be.
Crawlability and Indexing Errors
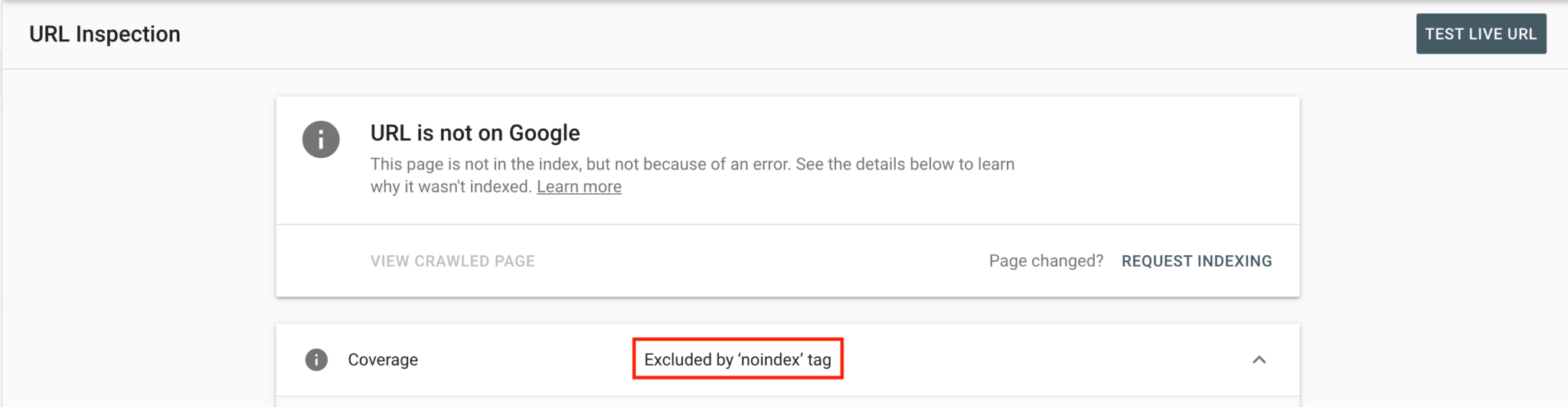
Crawlability issues represent the most fundamental technical SEO mistakes because they completely prevent search engines from discovering or properly indexing your content:
Robots.txt blocking: Incorrectly configured robots.txt files can inadvertently block search engines from crawling crucial pages. Always check your robots.txt to ensure you’re not blocking important content directories.
Improper noindex tags: Misplaced noindex directives prevent pages from appearing in search results even when they’re discovered by crawlers. According to data from SearchEngineJournal, this remains one of the most common critical errors in technical SEO audits.
HTTP to HTTPS redirection issues: 88% of sites fail to properly redirect HTTP to HTTPS, risking security penalties. This creates duplicate content issues and dilutes your site’s authority by splitting it between two versions.
Server errors: Recurring 5XX server errors or excessive 4XX errors signal to search engines that your site is unreliable, reducing crawl frequency and indexation rates.
Site Structure Problems That Confuse Search Engines
Poor site structure creates navigation barriers for both users and search engine crawlers:
Orphaned pages: Pages with no internal links pointing to them are difficult for search engines to discover and are unlikely to rank well.
Excessive site depth: Content buried more than 3-4 clicks from your homepage may receive less frequent crawling and lower prioritization.
Poor internal linking: Inadequate or disorganized internal linking prevents proper authority distribution throughout your site and makes it harder for crawlers to discover content.
Siloed content sections: Sections of your website that aren’t properly connected to your main navigation structure may be overlooked during crawls.
Security Issues Affecting Search Rankings
Security problems not only put your users at risk but directly impact your search visibility:
Missing HTTPS implementation: In 2025, HTTPS is no longer optional—sites without secure connections face significant ranking disadvantages and browser warnings.
Mixed content warnings: Pages serving both secure (HTTPS) and non-secure (HTTP) resources trigger browser warnings that damage user trust and search rankings.
Insecure forms: Contact or login forms without proper encryption create security vulnerabilities that search engines increasingly penalize.
How Page Experience Errors Damage Your SEO
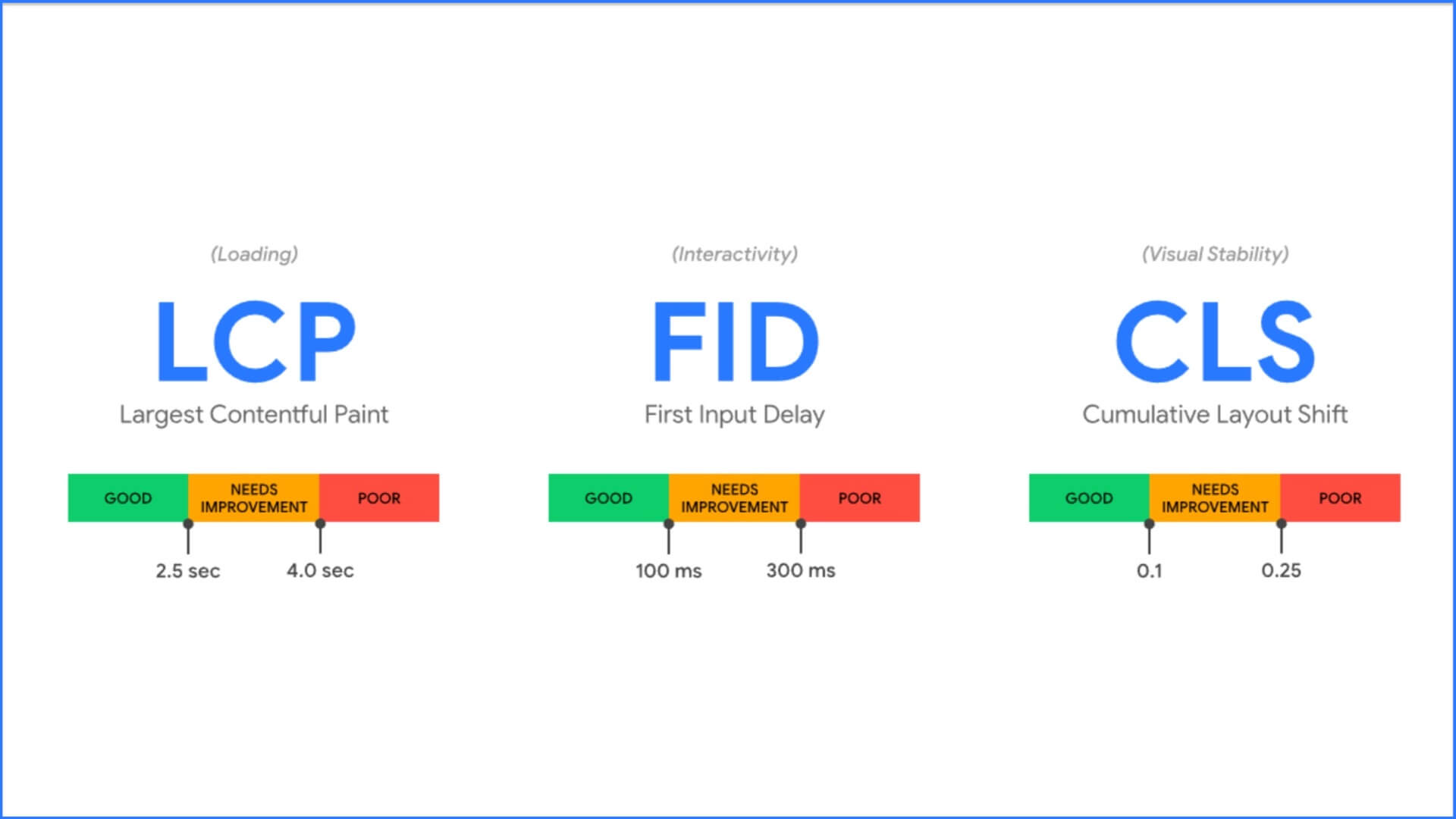
Page experience has become a critical ranking factor in 2025. Poor user experience metrics directly impact your search visibility, with Core Web Vitals (LCP, FID, CLS) now playing a crucial role in determining rankings.
Core Web Vitals Problems That Hurt Rankings
Core Web Vitals measure the real-world experience of users on your site:
Poor Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): When your page’s main content takes more than 2.5 seconds to load, users perceive your site as slow, increasing bounce rates. Data shows a 2-second delay leads to a 103% bounce rate increase.
Inefficient First Input Delay (FID): Pages that don’t respond quickly to user interactions (within 100ms) create frustration and signal poor performance to search engines.
High Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Unexpected movement of page elements during loading creates a poor user experience and directly impacts your Core Web Vitals scores.
Render-blocking resources: JavaScript and CSS files that block rendering extend load times and negatively impact all Core Web Vitals metrics.
Mobile Optimization Failures
With 70% of websites now indexed mobile-first, mobile optimization is non-negotiable:
Non-responsive design: Websites without responsive design provide a poor experience on mobile devices, directly impacting rankings in mobile search results.
Small touch elements: Clickable elements spaced too closely together or sized too small (under 48px) create usability problems on touch screens.
Small font sizes: Text smaller than 12px on mobile devices creates readability issues that harm user experience metrics.
Improper viewport configuration: Missing or incorrect viewport meta tags prevent proper scaling on mobile devices, creating horizontal scrolling issues.
Page Speed Issues Increasing Bounce Rates
Speed remains one of the most critical factors in both user experience and search rankings:
Uncompressed images: Large image files significantly slow page loading and waste bandwidth, particularly affecting mobile users.
Missing browser caching: Failing to leverage browser caching forces repeat visitors to download the same resources multiple times.
Unminified CSS/JavaScript: Bloated code files increase load times and resource consumption.
Server response time issues: Slow server response times (over 200ms) create a poor foundation for all other page loading processes.
Are These URL Structure Mistakes Hurting Your SEO?
URL structure mistakes create confusion for both users and search engines, leading to crawling inefficiencies, duplicate content issues, and poor user experience.
Problematic URL Parameters
URL parameter issues are particularly damaging for e-commerce and database-driven websites:
Excessive parameters: URLs with multiple parameters create crawling confusion and potential duplicate content.
Session IDs in URLs: Session identifiers in URLs generate millions of unique URLs for the same content, wasting crawl budget.
Tracking parameters without management: Analytics or tracking parameters create duplicate content when not properly managed with canonical tags or parameter settings in Search Console.
Faceted navigation parameters: Filter and sort parameters from faceted navigation can create millions of URL combinations if not properly controlled.
Redirect Chain Problems
Redirect issues waste crawl budget and dilute link equity:
Multiple hop redirects: Chains of redirects (A→B→C) slow down both users and crawlers, with 95.2% of websites facing this problem.
Temporary redirects for permanent changes: Using 302 (temporary) redirects for permanent changes prevents proper passing of link equity.
Redirect loops: Circular redirects that never resolve to content frustrate users and may cause search engines to drop pages from their index.
Mobile redirect errors: Improper implementation of mobile redirects creates a poor user experience and confuses search engines about content relationships.
Duplicate Content From URL Variations
URL variations creating duplicate content remain prevalent:
WWW vs. non-WWW versions: Sites accessible through both www and non-www versions without proper canonicalization split link equity.
Trailing slash inconsistency: Inconsistent use of trailing slashes in URLs without proper redirects creates duplicate content issues.
HTTP/HTTPS duplicates: Content accessible through both HTTP and HTTPS without proper redirection splits your site’s authority.
Case sensitivity issues: Servers that treat URLs with different letter cases as separate pages create duplicate content problems.
Why Is Your Content Not Properly Indexed?
Even excellent content can fail to appear in search results due to technical barriers preventing proper indexation.
JavaScript Rendering Issues
JavaScript-related problems have become increasingly common as websites rely more heavily on modern frameworks:
Client-side rendering dependencies: Content that relies entirely on client-side JavaScript may not be fully indexed, especially for complex applications.
JavaScript errors blocking content rendering: Script errors that prevent proper page rendering can make content invisible to search engines.
Lazy-loaded content without proper implementation: Content loaded through lazy-loading may be missed during crawling if not implemented with proper SEO considerations.
Single-page applications (SPAs) without SEO adaptations: SPAs without server-side rendering or dynamic rendering solutions often face indexing challenges.
XML Sitemap Errors
Sitemap problems reduce the effectiveness of this critical indexing tool:
Outdated sitemaps: Sitemaps that haven’t been updated after site changes fail to guide crawlers to new content.
Non-indexable URLs in sitemaps: Including blocked or noindexed URLs in your sitemap wastes crawl budget and reduces sitemap effectiveness.
Missing priority content: Failing to include your most important pages in the sitemap reduces discovery efficiency.
Incorrect canonical URLs: Sitemaps containing non-canonical URL versions create confusion about your preferred content versions.
Problems With Meta Directives
Meta directive issues send conflicting signals to search engines:
Missing meta descriptions: 25% of high-performing pages lack meta descriptions, reducing click-through rates from search results.
Duplicate title tags and descriptions: Non-unique meta information creates confusion about page relevance and content differentiation.
Conflicting directives: Contradictory signals like noindex tags with canonical tags pointing to the same page create indexing confusion.
Header tag problems: 59.5% of websites lack H1 tags and 51.3% have multiple H1 tags, harming content structure signals.
How Poor Implementation of Schema Markup Affects Rankings
Schema markup has become increasingly important for gaining rich results and enhanced visibility in search, yet many websites implement it incorrectly or miss opportunities entirely.
Missing Structured Data Opportunities
Neglecting schema markup means missing visibility opportunities:
Absence of organization schema: Missing basic organization markup prevents your brand information from appearing in knowledge panels.
Product schema omissions: E-commerce sites without product markup miss opportunities for rich results showing ratings, price, and availability.
Local business markup gaps: Local businesses without proper local business schema sacrifice visibility in map packs and local search results.
FAQ and how-to content without markup: Content that could earn expanded results through FAQ or how-to schema fails to stand out in search results.
Schema Markup Implementation Errors
Incorrect schema implementation prevents rich results from appearing:
Incomplete property sets: Missing required properties in schema markup prevents rich results from displaying.
Syntax errors: Coding errors in JSON-LD, microdata, or RDFa implementations invalidate your structured data.
Schema type mismatches: Using inappropriate schema types for your content (like using Article schema for product pages) confuses search engines.
Outdated schema formats: Using deprecated schema formats or properties reduces the effectiveness of your structured data.
Are These International SEO Technical Mistakes Costing You Traffic?
International SEO errors prevent proper targeting of content to specific countries or language audiences, fragmenting your global search presence.
Hreflang Tag Implementation Mistakes
Hreflang issues misdirect international traffic:
Missing return links: Hreflang tags without complete sets of reciprocal references between language/regional variants reduce effectiveness.
Incorrect language codes: Using improper language or country codes in hreflang attributes prevents proper language targeting.
Inconsistent implementation: Implementing hreflang inconsistently across your site creates confusion about content relationships.
Self-referencing errors: Failing to include self-referencing hreflang tags reduces the effectiveness of your international targeting.
Geotargeting Configuration Problems
Geotargeting mistakes harm international visibility:
Improper Search Console settings: Incorrect geographic targeting settings in Google Search Console misdirect your content to the wrong regions.
Mixed signals: Sending conflicting geotargeting signals through ccTLDs, hreflang tags, and Search Console settings confuses search engines.
IP-based redirects: Forcing users to specific language versions based on IP addresses prevents proper indexing of all country/language variants.
Missing international site structure: Lack of clear organization for language/country variants (through subdomains, subdirectories, or ccTLDs) creates confusion for both users and search engines.
How Technical SEO Mistakes Impact User Experience and Conversions
Technical SEO problems directly affect bottom-line business metrics, with page speed issues alone causing a 20% reduction in conversion rates for every second of mobile load time delay.
Accessibility Issues Reducing Site Usability
Accessibility problems hinder both user experience and SEO:
Missing alt attributes: 80.4% of websites lack proper alt attributes for images, limiting accessibility for visually impaired users and missing SEO opportunities.
Poor contrast ratios: Text with insufficient contrast against backgrounds creates readability issues for users with visual impairments.
Keyboard navigation problems: Sites that can’t be navigated via keyboard create barriers for users with mobility impairments.
Missing ARIA labels: Interactive elements without proper ARIA labels create confusion for screen reader users and send poor accessibility signals to search engines.
Navigation Problems Creating High Bounce Rates
Navigation issues directly impact engagement metrics:
Unintuitive site architecture: Confusing navigation structures increase cognitive load and frustrate users, increasing bounce rates.
Broken internal links: Links that lead to error pages or nowhere disrupt the user journey and waste link equity.
Mobile navigation barriers: Navigation elements that don’t translate well to mobile devices create friction points for mobile users.
Faceted navigation problems: Improperly implemented filters and faceted navigation create crawling issues while potentially frustrating users.
How to Identify and Fix the Top Technical SEO Mistakes
Effectively addressing technical SEO issues requires a systematic approach to identification, prioritization, and resolution.
Essential Technical SEO Audit Tools
The right tools make technical SEO diagnosis more efficient:
Google Search Console: Provides direct insights into indexing, mobile usability, Core Web Vitals, and crawling issues directly from Google.
Crawling tools: Software like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb can systematically identify technical issues across your entire website.
Page speed analysis tools: Lighthouse and PageSpeed Insights reveal specific performance bottlenecks affecting user experience.
Structured data testing tools: Schema markup validators help identify and fix structured data implementation errors.
Prioritizing Technical Fixes by Impact
Not all technical issues are equally important:
- Critical crawling and indexing barriers: Address robots.txt issues, server errors, and noindex problems first as they completely prevent discovery.
- User experience factors: Prioritize mobile optimization, page speed, and Core Web Vitals issues that directly impact rankings and conversions.
- Enhancement opportunities: Address schema markup, hreflang, and other enhancement opportunities after fixing fundamental issues.
- Maintenance concerns: Create processes to prevent technical debt from accumulating through future development.
Preventing Technical SEO Mistakes in Future Development
Proactive measures prevent new technical issues:
Technical SEO guidelines for developers: Create clear documentation of SEO requirements for your development team.
Pre-launch SEO checklists: Implement verification processes before launching new features or website updates.
Automated testing: Incorporate technical SEO checks into your CI/CD pipeline to catch issues before they reach production.
Regular technical audits: Schedule periodic comprehensive technical reviews to identify issues before they impact performance.
Conclusion: Taking Action on Technical SEO in 2025
Technical SEO remains the foundation of search success in 2025. Identifying and fixing these 40 critical technical mistakes can dramatically improve your website’s visibility, user experience, and conversion rates. The landscape continues to evolve, with increasing emphasis on page experience, mobile optimization, and structured data implementation.
